
Laravel is a free, open-source PHP framework designed to simplify web application development while maintaining high code quality and scalability. It provides developers with structured architecture, prebuilt components, and an ecosystem that accelerates development while ensuring maintainability. Laravel is widely adopted for building everything from small business websites à large-scale enterprise applications.
How Laravel Works?
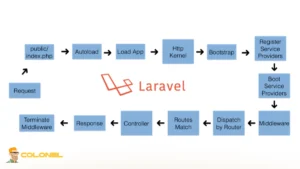
Laravel operates by adhering to the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, which separates data management, application logic, and presentation. Requests are routed to controllers, which interact with models to fetch or update data and then return views for the user interface. This separation keeps code organized, maintenable, and easy to scale.
The framework also provides built-in tools like Artisan for automating tasks, Eloquent ORM for intuitive database interactions, Blade templates for reusable layouts, and middleware for security and request handling. Ensemble, these features allow developers to build robust and scalable applications efficiently.
Core Features of Laravel
Laravel includes a set of features that make building modern PHP applications faster, more organized, et sécurisé. Its architecture emphasizes separation of concerns, while built-in tools reduce repetitive coding tasks and simplify database management. By integrating a robust command-line interface, template engine, and ORM system, Laravel ensures that both beginners and experienced developers can efficiently manage complex projects.
« Laravel provides built-in tools for routing, authentification, and database management, making PHP development faster and more secure. »_ Laravel News
Acheter maintenant
Hébergement Web WordPress
À partir de 3,99 $ / mensuel
MVC Architecture
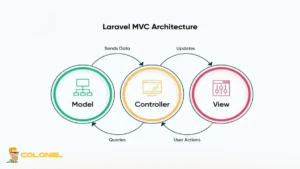
Laravel is designed around the Model-View-Controller architecture to enforce a clear separation of concerns at the core of the framework. This approach organizes the application into distinct layers so that data logic, request handling, and presentation do not overlap or interfere with each other.
En pratique, this structure improves long-term maintainability because changes in business logic do not directly affect the user interface, and front-end updates rarely require touching database logic. MVC also plays a critical role in team environments, where developers can work on models, controllers, and views in parallel without creating merge conflicts or architectural inconsistencies.
Artisan CLI
Artisan is Laravel’s command-line interface, built specifically to streamline development workflows and remove repetitive manual work from the process. Instead of writing boilerplate code or configuring common features by hand, developers rely on Artisan to standardize how core components are created and managed.
Beyond code generation, Artisan integrates tightly with Laravel’s internal systems such as migrations, planification, and application lifecycle management. This tight coupling allows developers to control complex operations through a single, consistent interface, which significantly reduces setup time and minimizes human error during development and deployment.
Blade Template Engine
Blade is Laravel’s native templating engine and focuses on keeping view logic simple, lisible, and reusable. It allows developers to construct dynamic interfaces without mixing heavy PHP logic into presentation files.

Serveur VPS pas cher
À partir de 2,99 $/mois
Where Blade becomes especially valuable is in layout management and content reuse. Template inheritance ensures that global structures like headers, navigation, and footers remain consistent across the application, while still allowing individual pages to inject their own content. Par conséquent, view files remain organized even as the project grows in size and complexity.
Eloquent ORM
Eloquent ORM provides an expressive, object-oriented layer for interacting with databases, replacing low-level query handling with model-driven logic. Each model acts as a direct representation of a database table and encapsulates both structure and behavior.
Instead of scattering SQL queries throughout the application, Eloquent centralizes data logic and relationships within models themselves. This makes complex queries easier to reason about, improves readability, and allows developers to work with related data in a more intuitive and maintainable way.

Built-In Authentication
Laravel includes a built-in authentication system that covers the most common security and access-control requirements without forcing developers to build these mechanisms from scratch.
- Route-level protection is handled through middleware that controls access before requests reach the application logic.
- Authentication workflows such as login, registration, and password recovery are standardized and easily extensible.
By providing these features out of the box, Laravel reduces security risks and ensures that user management follows well-established best practices from the very beginning of a project.

Hébergement VPS Windows
Remote Access & Full Admin
Creating a Model and Controller with Artisan
These commands generate models, controllers, and database migrations automatically, allowing developers to focus on implementing business logic rather than boilerplate code.
- Exemple: Creating a model, controller, and migration with Artisan
php artisan make:model User
php artisan make:controller UserController
php artisan migrateThis process creates a User model linked to the database, a UserController to handle business logic, and applies migrations to set up the database structure. It demonstrates how Laravel integrates code generation with database management.
Routing and Middleware in Laravel
Routing in Laravel directs incoming web requests to the appropriate controller or action. Middleware functions can be attached to routes to handle authentication, enregistrement, or other pre-processing tasks before the request reaches the controller. This architecture provides precise control over application behavior and security while keeping the route definitions clean.
Routes can also be organized in groups with shared middleware or namespaces, simplifying large-scale application management. Middleware ensures that repetitive tasks, such as verifying user permissions, are handled consistently across the application without duplicating code in each controller.
- Route Example with Authentication Middleware:
Route::get('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'show'])
->middleware('auth');- Accessing the Authenticated User:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth;
$user = Auth::user();This example demonstrates how Laravel protects routes and simplifies accessing the authenticated user, ensuring secure and maintainable application logic.
Security Features in Laravel
Security is a critical aspect of any modern web application, and Laravel incorporates multiple built-in protections to minimize vulnerabilities. The framework provides secure password hashing, CSRF protection, XSS safeguards, and SQL injection prevention by default. Developers can leverage these tools to create secure applications without manually implementing complex security layers.
With these features, Laravel ensures a secure development environment and helps businesses protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or attacks.
CSRF Protection
CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) protection in Laravel prevents malicious actors from tricking authenticated users into submitting unintended requests. In this type of attack, a user unknowingly performs actions while logged in, potentially compromising their account or data. Laravel mitigates this risk by requiring a unique CSRF token for every state-changing request, ensuring the form is submitted from the application itself and not from an external source.
This token is automatically generated by Laravel and stored in the user’s session. When a request is submitted, Laravel checks the token against the session value. If the token is missing or invalid, the request is blocked before reaching your application logic. This built-in mechanism allows developers to prevent many common attacks without manually implementing security measures.
Exemple: CSRF-protected form in Laravel
<form method="POST" action="/submit">
@csrf
<input type="text" name="title">
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>XSS Protection
XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) protection in Laravel prevents malicious scripts from executing in a user’s browser. These scripts usually originate from untrusted user input, and if rendered without filtering, they could compromise the security of your application or steal sensitive data.
Laravel’s Blade templating engine automatically escapes variables when rendering views. This means any content entered by a user is treated as plain text rather than executable code. Par conséquent, even if the input contains malicious JavaScript, it will not run in the browser.
This default behavior removes the need for developers to manually sanitize all output, reducing the risk of human error. Only in cases where raw HTML is intentionally required does the developer need to bypass this safety mechanism.
Real-World Applications of Laravel
Laravel’s flexibility allows it to support a wide variety of projects, from small-scale websites to complex enterprise systems. Developers use Laravel to build:
- commerce électronique Platforms: Tools like Bagisto and Aimeos are built on Laravel, offering multi-vendor support, inventory management, and API-driven commerce solutions.
- Content Management Systems: CMS platforms like Statamic leverage Laravel to provide dynamic content management, flat-file systems, and headless CMS capabilities.
- APIs and Web Services: Platforms like Treblle demonstrate Laravel’s use in creating robust APIs, with features for analytics, Surveillance en temps réel, and automated documentation.
- Custom Business Systems: Laravel powers ERP tools, CRM platforms, and internal business automation applications, thanks to its modular architecture and scalability.
Laravel’s ecosystem, including packages and libraries, makes it a preferred choice for businesses requiring tailored solutions without reinventing core functionality.
Scaling Laravel Applications
Applications built with Laravel can scale vertically or horizontally, depending on the business needs. Vertical scaling involves adding new modules or services within the application, while horizontal scaling uses load balancing, queues, and cloud infrastructure to handle increased traffic efficiently. Laravel’s modular architecture ensures new components integrate without breaking existing features, providing reliable growth for applications as user demands increase.
- Queue System Example:
php artisan queue:workQueues in Laravel allow background processing of tasks like email sending, file processing, or API calls, improving application performance and responsiveness.
Comparing Laravel with Other Solutions
Understanding how Laravel compares with alternatives helps highlight its strengths:
| Comparaison | Description |
| Laravel vs WordPress | WordPress is primarily a content management platform, ideal for blogs and simple sites. Laravel offers full control over backend logic, making it suitable for complex business applications. |
| Laravel vs Symfony | Symfony provides flexibility and scalability for long-term projects, but Laravel is faster to implement and easier for developers to learn, which is ideal for rapid application development. |
| Laravel vs CodeIgniter | CodeIgniter is lightweight and simple, but Laravel provides advanced features like Eloquent ORM, Blade, Artisan CLI, and integrated authentication out-of-the-box. |
| Laravel vs No-Code Platforms | No-code platforms allow rapid prototyping but often lack performance, personnalisation, et évolutivité. Laravel provides a future-proof solution for businesses needing robust, high-performance applications. |
Final Thoughts on Laravel
Laravel stands out as a PHP framework that balances simplicity, évolutivité, and robust functionality. Its modular architecture, built-in features, and active community support make it a top choice for developers building modern web applications. From content-rich websites to complex enterprise systems, Laravel offers a secure, flexible, and efficient foundation for projects of any size. Choosing Laravel ensures faster development, maintainable code, and a reliable path to scaling applications as business needs evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions About Laravel
Is Laravel easy to learn?
Oui, for developers with a basic understanding of PHP and MVC, Laravel is accessible thanks to comprehensive documentation, active community support, and abundant tutorials.
What types of applications can be built with Laravel?
Laravel is versatile, supporting eCommerce platforms, Apis, CMS solutions, internal business tools, and scalable web applications.
How does Laravel improve development speed and reduce costs?
By offering prebuilt modules, command-line automation, and database tools like Eloquent ORM, Laravel shortens development time and reduces the need for repetitive coding.
What security mechanisms does Laravel offer?
Laravel provides CSRF protection, XSS prevention, SQL injection safeguards, secure password hashing, and built-in authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Is Laravel a front-end or back-end framework?
Laravel is primarily a back-end framework, though it can integrate with front-end technologies like Vue or React to form a full-stack solution.
