A cloud migration strategy is a structured, business-driven plan for moving workloads from traditional infrastructure to cloud-based environments such as VPS and bare metal servers. Without a clearly defined cloud migration strategy, organizations face elevated risks, including downtime, security gaps, uncontrolled costs, and degraded application performance. This strategy serves as the architectural and operational blueprint, aligning infrastructure decisions with long-term business goals.
What Is a Cloud Migration Strategy
A cloud migration strategy outlines the process of systematically moving applications, data, and infrastructure components to cloud platforms while maintaining performance, Sicherheit, and compliance. It goes beyond technical execution and establishes decision frameworks for workload prioritization, architecture selection, and risk management.
For VPS and bare metal servers, this strategy clarifies whether workloads should be rehosted, replatformed, or refactored, and how virtualization layers such as KVM or Proxmox integrate with cloud-native services. A strong cloud migration strategy ensures that infrastructure choices support scalability without sacrificing predictability or control.

Why VPS and Bare Metal Require a Different Migration Approach
VPS and bare metal servers require a specialized cloud migration strategy because they sit at the intersection of control, Leistung, und Skalierbarkeit. Unlike fully abstracted public cloud services, these environments expose infrastructure-level decisions that directly impact latency, throughput, and security posture.
Bare metal servers provide maximum performance and isolation but demand careful planning around provisioning, Skalierung, and failover. VPS environments introduce flexibility through virtualization, yet still require deliberate capacity planning and network architecture. A generic cloud migration strategy designed for managed public cloud services often fails to address these nuances.

WordPress-Webhosting
Ab 3,99 $/Monat
For organizations running databases, high-traffic web platforms, or latency-sensitive workloads, VPS and bare metal migrations must prioritize:
- Workload placement
- Network topology
- Resource guarantees
This is why cloud migration strategy design must be infrastructure-aware rather than provider-centric.
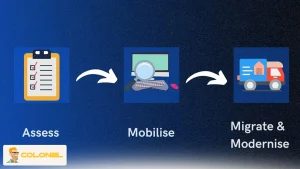
Comprehensive Assessment and Planning
A cloud migration strategy starts with a comprehensive assessment of existing workloads, dependencies, and operational constraints. This phase establishes factual clarity about what exists today and what is technically and economically feasible tomorrow.
Assessment is not a simple asset inventory. It involves analyzing application architectures, inter-service dependencies, data sensitivity, compliance requirements, and performance baselines. For VPS and bare metal environments, this step also evaluates hypervisor compatibility, storage performance characteristics, and network throughput requirements. Entsprechend AWS documentation:
“Successful cloud migrations begin with a profound understanding of the existing environment and clear business objectives that guide every migration decision.”
Skipping or compressing this phase almost guarantees cost overruns and architectural rework later in the migration process.

Günstiger VPS-Server
Ab 2,99 $/Monat
Workload Classification and Dependency Mapping
Workload classification defines how each application fits into the broader cloud migration strategy. Each workload must be evaluated based on business criticality, performance sensitivity, data compliance, and architectural complexity.
Dependency mapping identifies how applications communicate with databases, APIs, authentication systems, and third-party services. In VPS and bare metal migrations, undocumented dependencies are a leading cause of post-migration outages. Network flows, shared storage, and service-to-service communication must be explicitly mapped before migration begins.
Beispiel: A transactional application running on a VPS may rely on a low-latency database hosted on bare metal hardware. Migrating these components independently without accounting for latency and bandwidth constraints introduces avoidable performance degradation.

Choosing the Right Migration Model for Each Workload
Selecting the correct migration model is a foundational decision within any cloud migration strategy. Not all workloads benefit from the same approach, particularly in VPS and bare metal environments.
- Rehosting, often called lift-and-shift, moves workloads with minimal modification and is suitable for stable applications with predictable performance profiles. For bare metal workloads that demand consistent I/O performance, rehosting may preserve stability while deferring optimization.
- Refactoring involves architectural redesign and is best reserved for applications that must scale dynamically or integrate with cloud-native services.
- Replatforming introduces selective optimizations, such as migrating databases to optimized storage layers or updating operating systems. For VPS-based services, replatforming often delivers immediate efficiency gains without the cost of full refactoring.
A balanced cloud migration strategy applies different models based on workload characteristics rather than enforcing a single methodology.

Windows VPS-Hosting
Remote Access & Full Admin
Phased Migration as a Risk Control Mechanism
A phased migration approach reduces operational risk by breaking the cloud migration strategy into controlled, sequential stages. Rather than migrating all systems simultaneously, workloads are grouped into logical waves based on complexity and business impact. Here are the stages:
- Early phases typically include development environments or internal tools, allowing teams to validate assumptions and refine processes.
- Later phases address revenue-generating and mission-critical systems once operational confidence is established.
This method is especially important for VPS and bare metal migrations, where rollback options may be more limited than in fully managed cloud platforms.
Microsoft’s Cloud Adoption Framework emphasizes this approach, stating that iterative migration reduces failure rates and improves long-term adoption outcomes.
Governance and Compliance as Strategic Foundations
Governance defines how decisions are made, enforced, and audited throughout the cloud migration strategy. Without governance, VPS and bare metal environments quickly accumulate configuration drift, security gaps, and cost inefficiencies. Governance includes:
- Access control policies
- Network segmentation standards
- Naming conventions
- Compliance enforcement mechanisms
For regulated industries, governance also ensures adherence to standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS during and after migration.
Embedding governance into the migration strategy ensures that every newly deployed VPS or bare metal server conforms to predefined security and operational standards. This prevents the cloud environment from becoming less controlled than the on-premises infrastructure it replaces.
Cost Optimization and FinOps in Cloud Migration
Cost optimization in a cloud migration strategy means maintaining financial control while scaling VPS and bare metal infrastructure. Unlike traditional data centers with fixed costs, cloud environments introduce variable spending that must be actively governed.
For VPS workloads, overprovisioning is one of the most common cost leaks. Selecting instance sizes based on real usage metrics rather than peak assumptions reduces waste significantly. Bare metal servers require a different approach, focusing on workload consolidation, predictable billing models, and long-term capacity planning.
A FinOps-driven cloud migration strategy establishes cost visibility from day one. Teams monitor usage at the service and workload level, enforce budgets, and align infrastructure decisions with business value rather than technical convenience. This discipline ensures that performance gains do not come at the expense of uncontrolled spending.
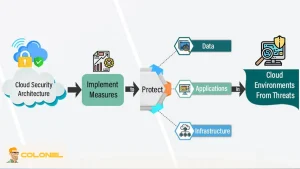
Security Architecture During Cloud Migration
Security in a cloud migration strategy must be designed before workloads move, not retrofitted afterward. VPS and bare metal environments expose low-level configuration choices that directly affect attack surfaces and compliance posture.
Network segmentation is the first security control. Isolating public-facing services, internal applications, and data layers limits the blast radius in case of compromise. Access control policies must enforce least-privilege principles across operating systems, hypervisors, and management interfaces.
Data protection is equally critical. Encryption at rest and in transit ensures that sensitive information remains protected during migration phases. A well-structured cloud migration strategy treats security controls as architectural components rather than operational add-ons, preserving trust and regulatory alignment throughout the transition.
Überwachung, Observability, and Performance Validation
Monitoring validates whether a cloud migration strategy delivers its promised outcomes. Without observability, performance regressions and resource inefficiencies remain invisible until they impact users.
For VPS and bare metal servers, monitoring must extend beyond application metrics. The following require continuous observation:
- CPU scheduling behavior
- Disk IOPS
- Memory pressure
- Network latency
Establishing baseline metrics before migration allows teams to compare post-migration performance objectively.
Observability tools also support faster incident response. When issues arise, engineers trace problems across infrastructure and application layers without guesswork. This feedback loop enables continuous optimization and ensures that the cloud migration strategy evolves with real operational data.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning
Disaster recovery is a core pillar of any serious cloud migration strategy. VPS and bare metal platforms offer flexibility, but resilience must be deliberately engineered.
Backup policies define how data is protected, where it is stored, and how quickly it can be restored. Replication strategies determine whether workloads can fail over to alternate locations with minimal disruption. For bare metal environments, this often involves standby capacity or rapid reprovisioning models.
Business continuity planning ensures that recovery objectives align with business tolerance for downtime and data loss. A migration strategy that ignores these considerations may reduce infrastructure costs while increasing operational risk, undermining its strategic value.
Application Modernization as a Strategic Extension
Application modernization is not mandatory for every cloud migration strategy, but it often becomes a logical next step. Once workloads run reliably on VPS or bare metal infrastructure, teams gain the flexibility to improve architectures incrementally.
Modernization may involve decoupling monoliths, introducing container orchestration, or adopting managed databases where appropriate. These changes improve scalability and deployment speed without requiring a full rewrite.
Choosing the Right Infrastructure Model Post-Migration
After migration, organizations reassess whether workloads belong on VPS, blankes Metall, or a hybrid combination. This decision is part of the ongoing cloud migration strategy rather than its conclusion.
- VPS platforms excel for scalable services with variable demand.
- Bare metal remains ideal for performance-intensive databases, analytics engines, and specialized workloads.
- Hybrid models balance cost efficiency with deterministic performance.
The ability to make these choices dynamically is one of the greatest strengths of a well-executed migration strategy. Infrastructure becomes an adaptable resource rather than a fixed constraint.

Why a Structured Cloud Migration Strategy Delivers Long-Term Value
A cloud migration strategy succeeds when it transforms infrastructure into a predictable, scalable foundation for growth. VPS and bare metal environments offer control and performance, but only disciplined planning converts these capabilities into business outcomes.
Organizations that invest in structured migration reduce operational friction, improve security posture, and gain financial clarity. More importantly, they establish an infrastructure platform that supports innovation rather than resisting it.
Cloud migration is not a one-time event. It is an evolving strategy that adapts as technologies, Arbeitsbelastungen, and business priorities change. When designed correctly, it becomes a durable competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cloud Migration Strategy
What is a cloud migration strategy?
A cloud migration strategy is a structured plan for moving applications and infrastructure to cloud platforms while controlling cost, Leistung, und Sicherheit.
Is VPS or bare metal better for cloud migration?
Both are suitable depending on workload needs, with VPS favoring scalability and bare metal prioritizing performance and isolation.
Does cloud migration always reduce costs?
Not automatically, but a well-managed cloud migration strategy prevents waste and aligns spending with actual usage.
How long does a cloud migration typically take?
Timelines vary based on complexity, but phased migrations often span several weeks to months.
Can legacy applications be migrated without modification?
Ja, many legacy workloads can be rehosted initially and modernized later as part of the migration strategy.
