Node.js ist eine JavaScript-Laufzeitumgebung, die es Entwicklern ermöglicht, JavaScript-Code außerhalb des Browsers auszuführen, hauptsächlich auf dem Server. Dadurch ist ein schneller Aufbau möglich, skalierbar, und netzwerkzentrierte Anwendungen in einer einzigen Sprache. Heutzutage ist es von entscheidender Bedeutung, zu verstehen, was Node.js ist, da es viele moderne Backend-Systeme gibt, APIs, und Cloud-Dienste basieren auf ihrem Architekturmodell und nicht auf traditionellen Serverparadigmen.
Was ist Node.js??
Node.js ist eine Open-Source-Lösung, Plattformübergreifende JavaScript-Laufzeit, die auf der V8-Engine von Chrome basiert und die Ausführung von JavaScript auf der Serverseite ermöglicht. Bei der Beantwortung dessen, was Node.js in seiner einfachsten Form ist, Man kann sie als die Umgebung beschreiben, die JavaScript von einer reinen Browsersprache in ein vollständiges Backend-Entwicklungstool verwandelt hat.
Node.js führt JavaScript-Code mit hoher Geschwindigkeit aus, da es dieselbe Engine nutzt, die auch von modernen Browsern verwendet wird, aber es beseitigt die Browserabhängigkeit vollständig. Dadurch können Entwickler bauen Server, APIs, und Tools auf Systemebene, die JavaScript verwenden, und profitieren gleichzeitig von starken Leistungsmerkmalen und einem riesigen Paket-Ökosystem.
Aus praktischer Sicht, Node.js hat die Backend-Entwicklung verändert, indem es Leistungsengpässe behoben hat, die durch das Blockieren von E/A und Thread-basierter Parallelität verursacht wurden. Anstatt durch Hinzufügen von Threads zu skalieren, Node.js skaliert durch effizientes Verwalten von Ereignissen, was direkt auf die Anforderungen von Echtzeitanwendungen abgestimmt ist, Mikrodienste, und stark frequentierte Plattformen.

Warum Node.js erstellt wurde
Node.js wurde entwickelt, um Skalierbarkeits- und Leistungseinschränkungen herkömmlicher Webserver zu lösen. Um vollständig zu verstehen, was Node.js ist, Es ist wichtig, das Problem zu verstehen, für das es entwickelt wurde.

WordPress Web Hosting
Ab 3,99 USD/monatlich
Herkömmliche Serverarchitekturen stützten sich stark auf Blockierungsvorgänge und Thread-pro-Anfrage-Modelle. Als der Verkehr zunahm, Diese Systeme verbrauchten übermäßig viel Speicher und CPU-Ressourcen. Node.js hat eine nicht blockierende Funktion eingeführt, Ereignisgesteuerter Ansatz, der es Servern ermöglichte, Tausende gleichzeitiger Verbindungen effizient zu verarbeiten, sogar auf bescheidener Hardware.
Wie Node.js intern funktioniert
Node.js kombiniert eine schnelle JavaScript-Engine mit einem ereignisgesteuerten Ausführungsmodell, das blockierende Vorgänge vermeidet. Dieses interne Design ist die Grundlage dafür, dass Node.js für skalierbare Netzwerkanwendungen geeignet ist.
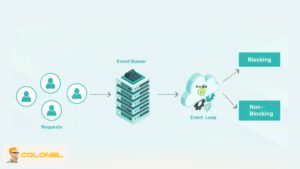
Wenn eine Node.js-Anwendung gestartet wird, Es führt das anfängliche Skript aus und tritt dann automatisch in eine Ereignisschleife ein. Aufgaben wie das Lesen von Dateien, Datenbankabfragen, oder Netzwerkanfragen werden an Hintergrundarbeiter delegiert. Sobald diese Vorgänge abgeschlossen sind, Rückrufe werden zurück in die Ereigniswarteschlange gestellt, Dadurch bleibt der Hauptthread jederzeit reaktionsfähig.
Die Ereignisschleife praktisch erklärt
Die Ereignisschleife ist der Mechanismus, der es Node.js ermöglicht, asynchrone Aufgaben zu verarbeiten, ohne die Ausführung zu blockieren. Jede genaue Erklärung dessen, was Node.js ist, muss ein klares Verständnis dieses Konzepts beinhalten.
Anstatt darauf zu warten, dass der Betrieb abgeschlossen ist, Node.js registriert Rückrufe und führt weiterhin anderen Code aus. Die Ereignisschleife sucht kontinuierlich nach abgeschlossenen Aufgaben und führt deren Rückrufe nacheinander aus. Wenn keine Aufgaben mehr übrig sind, Der Vorgang wird automatisch beendet. Dieses Verhalten spiegelt Browser-JavaScript wider, wo Entwickler selten direkt mit der Ereignisschleife interagieren.
Blockierende vs. nicht blockierende E/A in Node.js
Node.js basiert auf nicht blockierendem I/O, Dies wirkt sich direkt auf die Anwendungsleistung und Skalierbarkeit aus. Durch das Blockieren von E/A wird die Ausführung angehalten, bis eine Aufgabe abgeschlossen ist, während die nicht blockierende E/A es der Anwendung ermöglicht, weiter ausgeführt zu werden.

Günstiger VPS -Server
Ab 2,99 USD/monatlich
In Node.js, Die meisten Standardbibliotheksfunktionen verwenden standardmäßig nicht blockierende Vorgänge. Dadurch wird sichergestellt, dass langsame Aufgaben wie Festplattenzugriffe oder Datenbankabfragen den Server nicht daran hindern, andere Anfragen zu verarbeiten. Diese Designwahl ist ein Hauptgrund dafür, dass Node.js bei I/O-intensiven Arbeitslasten außergewöhnlich gut funktioniert.
Asynchrone Programmierung in Node.js
Node.js setzt auf asynchrone Programmierung, um die Reaktionsfähigkeit unter Last aufrechtzuerhalten. Es wäre unvollständig, zu verstehen, was Node.js ist, ohne die asynchrone Ausführung zu verstehen.
Asynchroner Code ermöglicht es Node.js, Aufgaben zu starten und sofort fortzufahren, ohne auf Ergebnisse warten zu müssen. Entwickler drücken diese Logik mithilfe von Rückrufen aus, verspricht, oder async/await-Syntax. Dieses Modell ermöglicht die effiziente Abwicklung mehrerer gleichzeitiger Vorgänge, was für APIs unerlässlich ist, Echtzeitdienste, und datengesteuerte Anwendungen.
Warum Node.js keine Thread-basierte Parallelität verwendet
Node.js vermeidet herkömmliche Thread-basierte Parallelität, um Komplexität und Overhead zu reduzieren. Aus Sicht des Systemdesigns, Diese Auswahl definiert, was Node.js als Laufzeit ist.
Thread-basierte Server erfordern Synchronisierungsmechanismen, die das Risiko von Deadlocks und Leistungseinbußen erhöhen. Node.js beseitigt diese Bedenken durch die Verwendung einer Single-Threaded-Ereignisschleife, in der Vorgänge selten blockieren. Entwickler müssen keine Sperren und keinen gemeinsam genutzten Speicher verwalten, Dies vereinfacht die Anwendungslogik und verbessert die Zuverlässigkeit.

Windows VPS -Hosting
Remote Access & Full Admin
HTTP als Kernfunktion von Node.js
HTTP ist ein erstklassiger Bürger in Node.js, kein nachträglicher Einfall. Diese Designentscheidung spielt eine wichtige Rolle dafür, warum Node.js häufig für Webdienste verwendet wird.
Das integrierte HTTP-Modul unterstützt Streaming, Kommunikation mit geringer Latenz, und eine detaillierte Kontrolle über die Bearbeitung von Anfragen. Durch die tiefe Einbettung von HTTP in die Laufzeit, Mit Node.js können Entwickler Webserver und APIs erstellen, ohne auf umfangreiche Frameworks angewiesen zu sein, was die Leistung und Flexibilität verbessert.
Multi-Core-Verarbeitung in Node.js
Obwohl Node.js eine Single-Threaded-Ereignisschleife verwendet, Es ist nicht auf einen einzelnen CPU-Kern beschränkt. Um genau zu verstehen, was Node.js ist, muss man verstehen, wie es sich über die Hardware hinweg skaliert.
Node.js stellt untergeordnete Prozesse und Clustering-Mechanismen bereit, die die Verteilung von Arbeitslasten auf mehrere Kerne ermöglichen. Diese Prozesse können Netzwerkports gemeinsam nutzen und effizient kommunizieren, Dies ermöglicht eine horizontale Skalierung und bewahrt gleichzeitig die Einfachheit des ereignisgesteuerten Modells.
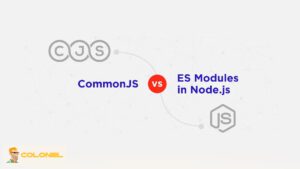
CommonJS- und ECMAScript-Module in Node.js
Node.js unterstützt mehrere Modulsysteme, die definieren, wie Code organisiert und wiederverwendet wird. Diese Flexibilität ist ein wichtiger Bestandteil der modernen Node.js-Entwicklung.
Historisch, Node.js basierte auf CommonJS-Modulen, die require und module.exports verwenden. In jüngerer Zeit, ECMAScript-Module wurden eingeführt, um Node.js an moderne JavaScript-Standards anzupassen. Durch die Unterstützung beider Systeme können Entwickler Legacy-Projekte beibehalten und gleichzeitig neuere Muster schrittweise übernehmen.
Was können Sie mit Node.js erstellen?
Node.js unterstützt eine Vielzahl von Anwendungstypen, Damit ist es eine der vielseitigsten Backend-Laufzeiten, die heute verfügbar sind. Es wird häufig zum Erstellen von REST-APIs verwendet, Mikrodienste, Echtzeit-Kommunikationssysteme, Streaming-Plattformen, und Befehlszeilentools. Dank seiner nicht blockierenden Architektur kann es effizient mit einer großen Anzahl gleichzeitiger Benutzer umgehen, was für moderne Webanwendungen unerlässlich ist.
Node.js in realen Architekturen
Node.js wird aufgrund seiner Effizienz und Flexibilität häufig in modernen Anwendungsarchitekturen verwendet. Im praktischen Einsatz, Was Node.js ist, wird klarer, wenn man untersucht, wie es in reale Systeme passt.
Node.js fungiert häufig als API-Schicht in Microservice-Architekturen, Umgang mit der Authentifizierung, Routenführung, und Datenaggregation. Es wird auch häufig als Echtzeit-Kommunikationsschicht für WebSockets und ereignisgesteuerte Workflows verwendet. In Cloud-native Umgebungen, Node.js lässt sich nahtlos in Container integrieren, Orchestrierungsplattformen, und serverlose Infrastruktur.
Warum Node.js weit verbreitet ist
Node.js erfreute sich großer Beliebtheit, da es sich perfekt an die sich entwickelnden Webanforderungen anpasste. Da Anwendungen interaktiver und datenintensiver wurden, Traditionelle Servermodelle hatten Mühe, mitzuhalten.
Durch die Aktivierung von JavaScript sowohl auf dem Client als auch auf dem Server, Node.js reduzierte Entwicklungsreibungen und beschleunigte Produktzyklen. Seine Leistungsmerkmale und sein starkes Ökosystem haben seine Position als zentrale Backend-Technologie weiter gestärkt.
Node.js-Versionen und die Bedeutung von LTS-Versionen
Node.js folgt einem strukturierten Release-Zyklus, der sich direkt auf die Stabilität auswirkt, Sicherheit, und langfristige Wartbarkeit. Etwa alle sechs Monate wird eine neue Hauptversion von Node.js veröffentlicht, Einführung neuer Funktionen und Änderungen. Jedoch, Nicht alle Versionen sind für den Produktionseinsatz geeignet.
Langfristiger Support (LTS) Versionen erhalten erweiterte Sicherheitspatches und Fehlerbehebungen, Dies macht sie zur bevorzugten Wahl für Unternehmenssysteme, kommerzielle Anwendungen, und geschäftskritische Dienste. Die Verwendung einer LTS-Version reduziert das Upgrade-Risiko und gewährleistet ein vorhersehbares Verhalten im Laufe der Zeit.
Wie eine Node.js-Anfrage Schritt für Schritt verarbeitet wird
Ein Node.js-Anforderungslebenszyklus zeigt, wie die Laufzeit die Parallelität effizient handhabt, ohne die Ausführung zu blockieren. Dieser Betriebsablauf erklärt, was Node.js über theoretische Definitionen hinausgeht.
Wenn eine Anfrage eintrifft, Node.js registriert es in der Ereignisschleife und bestimmt, ob die Aufgabe eine Berechnung oder E/A beinhaltet. CPU-gebundene Logik wird sofort ausgeführt, während E/A-Vorgänge wie Datenbankabfragen an Hintergrundarbeiter delegiert werden. Sobald der Vorgang abgeschlossen ist, sein Rückruf wird zur Ausführung in die Warteschlange gestellt. Dieser Prozess stellt sicher, dass der Server auch unter hoher Last reaktionsfähig bleibt.
Um diesen Ablauf zu verdeutlichen, Der Prozess kann wie folgt zusammengefasst werden:
- Die Anfrage gelangt in die Ereignisschleife und wird ausgewertet.
- E/A-intensive Aufgaben werden asynchron ausgelagert.
- Die Ereignisschleife verarbeitet weiterhin andere Anforderungen.
- Abgeschlossene Aufgaben geben Ergebnisse über Rückrufe oder Versprechen zurück.
- Die Antwort wird gesendet, ohne andere Verbindungen zu blockieren.
Stärken und Grenzen von Node.js
Node.js verfügt neben technischen Einschränkungen auch über klar definierte Stärken, und das Verständnis beider ist wichtig, um die Frage, was Node.js in der realen Backend-Entwicklung ist, genau zu beantworten. Gleichzeitig, Sein Ausführungsmodell führt zu Einschränkungen beim Umgang mit CPU-intensiven Vorgängen, Dies bedeutet, dass architektonische Entscheidungen eine entscheidende Rolle für eine erfolgreiche Einführung spielen. Betrachten Sie die folgende Tabelle:
| Aspekt | Stärken | Einschränkungen |
| Parallelitätsmodell | Nicht blockierend, Die ereignisgesteuerte Architektur ermöglicht die effiziente Nutzung Tausender gleichzeitiger Verbindungen | Eine Single-Thread-Ereignisschleife kann durch CPU-intensive Aufgaben blockiert werden |
| Leistungsprofil | Hervorragender Durchsatz für I/O-intensive Anwendungen wie APIs und WebSockets | Schlechte Eignung für umfangreiche Berechnungen ohne Arbeitsthreads oder externe Dienste |
| Skalierbarkeit | Einfache horizontale Skalierung durch Clustering und Microservices | Die vertikale Skalierung ist durch die Single-Core-Ausführung pro Prozess begrenzt |
| Entwicklungseffizienz | Die gemeinsame JavaScript-Sprache im Frontend und Backend beschleunigt die Entwicklung | Komplexe asynchrone Abläufe können die Wartbarkeit in großen Codebasen beeinträchtigen |
Node.js im Vergleich zu anderen Backend-Technologien
Node.js unterscheidet sich grundlegend von herkömmlichen Backend-Plattformen in der Art und Weise, wie es Ausführung und Parallelität handhabt, nicht nur in der Sprache, die es verwendet. Um Node.js richtig zu kontextualisieren, Es muss mit etablierten Backend-Technologien wie Java verglichen werden, .NETTO, Python, Los geht.
| Technologie | Parallelitätsmodell | Praktischer Vergleich mit Node.js |
| Node.js | Ereignisschleife mit asynchroner Ausführung | Geringerer Speicheraufwand und hohe Effizienz für gleichzeitige E/A-Vorgänge |
| Java | Threadbasierte Parallelität | Stark für CPU-intensive Arbeitslasten, aber höheren Ressourcenverbrauch |
| .NETTO | Verwaltetes Multithreading | Zuverlässig für Unternehmenssysteme, typischerweise langsamere Iterationszyklen |
| Python | GIL-eingeschränkte Parallelität | Einfacher für Datenaufgaben, aber geringerer Durchsatz für gleichzeitige Verbindungen |
| Gehen | Goroutinen und Kanäle | Starkes natives Parallelitätsmodell, kleineres Web-Ökosystem als Node.js |
Paketverwaltung und das Node.js-Ökosystem
Das Node.js-Ökosystem wird von npm betrieben, die größte Paketregistrierung in der Softwarewelt. Dieses Ökosystem spielt eine wichtige Rolle dabei, warum die Akzeptanz von Node.j weiter zunimmt.
npm bietet Zugriff auf Bibliotheken für Web-Frameworks, Datenbanktreiber, Sicherheitstools, und Automatisierungsdienstprogramme. Die Verwendung offizieller Node.js-Paketbereiche gewährleistet Authentizität und reduziert Sicherheitsrisiken. Dieses Ökosystem ermöglicht es Entwicklern, komplexe Systeme schnell zusammenzustellen, ohne die Kernfunktionalität neu zu erfinden.
Sicherheitsüberlegungen in Node.js-Anwendungen
Sicherheit ist ein kritischer Aspekt von Node.js-Produktionssystemen. Um verantwortungsvoll zu verstehen, was Node.js ist, muss man wissen, wie man es richtig sichert.
Node.js-Anwendungen müssen Eingaben validieren, Verwalten Sie Abhängigkeiten sorgfältig, und vermeiden Sie unsichere Muster wie synchrone Blockierungsaufrufe in kritischen Pfaden. Benutzen Https, Umgebungsvariablen für Geheimnisse, und offizielle Node.js-Quellen reduzieren die Angriffsflächen. Aufgrund des schnelllebigen Ökosystems sind regelmäßige Abhängigkeitsprüfungen und -aktualisierungen unerlässlich.
Strategien zur Leistungsoptimierung für Node.js
Die Leistungsoptimierung von Node.j konzentriert sich auf die Aufrechterhaltung eines nicht blockierenden Verhaltens und einer effizienten Ressourcennutzung. Dieser Aspekt hat direkten Einfluss auf die Skalierbarkeit.
Zu den wichtigsten Optimierungsstrategien gehört die Vermeidung synchroner E/A, Verwenden von Verbindungspooling für Datenbanken, Implementierung von Caching-Ebenen, und Überwachung der Latenz der Ereignisschleife. Profiling-Tools helfen dabei, Engpässe frühzeitig zu erkennen, Sicherstellen, dass die Leistung auch bei steigendem Datenverkehr stabil bleibt.
Maßgebliche Perspektiven auf Node.js
Branchenexperten und offizielle Dokumentationen betonen immer wieder die Skalierbarkeit und Effizienz von Node.j. Nach Angaben des Beamten Node.js-Dokumentation:
„Node.js wurde entwickelt, um skalierbare Netzwerkanwendungen ereignisgesteuert zu erstellen, nicht blockierendes I/O-Modell.“
Zusätzlich, Die OpenJS Foundation betont seine Rolle in der modernen Infrastruktur:
„Node.js ermöglicht es Entwicklern, leistungsstarke Produkte zu erstellen, skalierbare Systeme mit JavaScript plattformübergreifend.“
Wenn Node.js die richtige Wahl ist?
Node.js ist die richtige Wahl, wenn die Anwendungsanforderungen mit seinen architektonischen Stärken übereinstimmen. Die Bestimmung, wofür Node.js geeignet ist, hängt von den Workload-Eigenschaften ab.
Anwendungen, die Echtzeitkommunikation beinhalten, Hohe Parallelität der Anforderungen, Streaming-Daten, oder API-gesteuerte Systeme profitieren am meisten. Umgekehrt, Anwendungen, die von umfangreichen numerischen Berechnungen dominiert werden, erfordern möglicherweise ergänzende Technologien neben Node.js.
Häufig gestellte Fragen zu Node.js
Wofür wird Node.js hauptsächlich verwendet??
Node.js wird hauptsächlich zum Aufbau skalierbarer Backend-Dienste verwendet, APIs, Echtzeitanwendungen, und Entwicklungstools, die eine hohe Parallelität erfordern.
Ist Node.js eine Programmiersprache??
Node.js ist keine Sprache; Es handelt sich um eine JavaScript-Laufzeitumgebung, die JavaScript außerhalb des Browsers ausführt.
Kann Node.js hohen Datenverkehr bewältigen??
Ja, Node.js ist darauf ausgelegt, eine große Anzahl gleichzeitiger Verbindungen mithilfe nicht blockierender E/A effizient zu verarbeiten.
Ist Node.js für Unternehmensanwendungen geeignet??
Ja, bei Verwendung mit LTS-Versionen und der richtigen Architektur, Node.js ist in Unternehmenssystemen weit verbreitet.
