
OpenVPN Access Server is a powerful and easy-to-use VPN solution that is designed to offer a secure and reliable way to access a private network from the internet. OpenVPN Access Server is a powerful solution that offers a combination of strong encryption, flexible authentication, and easy management in a single, streamlined solution. With the installation and configuration of OpenVPN Access Server, organizations can provide secure and encrypted connections for remote workers, as well as protect sensitive data transmitted over the internet, while also providing secure access to the internal network from anywhere.
What Is OpenVPN Access Server and Why Use It for Secure Remote Access?
OpenVPN Access Server is a business-focused VPN solution built on the widely trusted OpenVPN protocol. It is designed to provide secure, encrypted remote access to private networks over the internet. Unlike basic VPN implementations that require complex manual configuration, OpenVPN Access Server offers a user-friendly web-based management interface, centralized control, and scalable deployment options for organizations of all sizes.
In today’s digital landscape, remote work, hybrid offices, and cloud infrastructure are standard. Employees, Entwickler, and system administrators frequently need access to internal systems such as file servers, Datenbanken, control panels, and internal applications. Exposing these services directly to the internet significantly increases security risks. This is where OpenVPN Access Server becomes essential.
By creating an encrypted tunnel between the user’s device and the private network, OpenVPN Access Server ensures:
- Data confidentiality through strong encryption
- Secure authentication of users and devices
- Protection against man-in-the-middle attacks
- Safe access over public Wi-Fi networks

Key Benefits of Installing OpenVPN Access Server VPN
Deploying OpenVPN Access Server VPN provides both security and operational advantages. It goes beyond simple encrypted connections and delivers a complete remote access framework.

WordPress-Webhosting
Ab 3,99 $/Monat
Here are the primary benefits:
Strong Encryption Standards
OpenVPN uses SSL/TLS-based encryption to secure data in transit, ensuring confidentiality and integrity.
Centralized User Management
Administrators can create, disable, and manage users from a single interface.
Multi-Platform Client Support
Compatible with Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS devices.
Skalierbarkeit
Suitable for small teams as well as large enterprises.
Granular Access Control
Define which users can access specific internal subnets or services.

Günstiger VPS-Server
Ab 2,99 $/Monat
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Unterstützung
Adds an additional security layer beyond username and password.
Reduced Attack Surface
Internal services remain private and are not exposed to the public internet.
From a business continuity perspective, a VPN ensures employees can securely access resources during emergencies, travel, or remote work scenarios. For IT teams managing cloud servers or VPS environments, it creates a secure administrative channel without exposing SSH or database ports publicly.
If you are also interested in strengthening your overall infrastructure security, you may want to read our related article: Boost Email Security with SPF, DKIM, DMARC, which explains how to secure email communication alongside network security.
Together, network-level and email-level security create a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.


Windows VPS-Hosting
Remote Access & Full Admin
System Requirements for OpenVPN Access Server Installation
Before installing OpenVPN Access Server, it is important to ensure your server environment meets the necessary technical requirements. The software is typically deployed on Linux-based systems and can run on both physical servers and virtual machines, including cloud VPS instances.
Below is an overview of typical system requirements:
| Component | Minimum Requirement | Recommended for Production |
|---|---|---|
| Betriebssystem | Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL, CentOS | Ubuntu LTS (latest) |
| CPU | 1 Kern | 2+ Cores |
| RAM | 1 GB | 2–4 GB |
| Storage | 8 GB | 20+ GB-SSD |
| Netzwerk | Public IP Address | Static Public IP |
| Ports Required | 443, 943, 1194 (default) | Properly configured firewall |
For production deployments:
- Use a clean, updated Linux installation
- Configure a static public IP address
- Ensure firewall rules allow required ports
- Maintain system updates for security patches
Running OpenVPN Access Server in a cloud environment (such as a VPS or dedicated server) is common practice. Make sure the provider allows custom firewall configurations and persistent networking rules.
How to Download OpenVPN Access Server on Linux
Downloading OpenVPN Access Server is straightforward and can be done directly from the official repository. The installation package depends on your Linux distribution.
Typically, the process involves:
Identifying your Linux distribution version
- Adding the official OpenVPN repository
- Updating your package list
- Installing the Access Server package
For Ubuntu systems, this usually involves using apt after adding the OpenVPN repository key. For RHEL or CentOS-based systems, yum or dnf is used instead.
It is highly recommended to:
- Download packages only from the official OpenVPN source
- Avoid third-party mirrors
- Verify repository authenticity
- Keep your system updated before installation
Nach der Installation, the service usually starts automatically, and you will receive an admin interface URL.
Security note: Always perform installation on a secure server environment. Avoid deploying VPN software on shared hosting platforms. A VPS or dedicated server provides better isolation and control.

Step-by-Step Guide to Install OpenVPN Access Server
Installing OpenVPN Access Server is designed to be simple, especially compared to traditional OpenVPN manual setups.
Here is a high-level installation flow:
- Update your Linux system packages
- Add the official OpenVPN repository
- Install the OpenVPN Access Server package
- Set or update the admin password
- Access the web admin panel
- Verify service status
After installation completes, the terminal usually displays:
- Admin Web UI URL
- Client Web UI URL
- Default admin username
You can then set the admin password using system commands.
Once the admin interface is accessible, configuration becomes graphical and significantly easier.
For infrastructure teams running containerized environments, combining VPN access with container security is highly recommended. You may also find our article Secure Docker Container Hosting Services useful if your organization uses Docker in production.
Initial Setup and Web-Based Configuration of OpenVPN Access Server
Once installed, OpenVPN Access Server provides a web-based admin interface, typically accessible via:
https://your-server-ip:943/admin
The initial login uses the admin account created during installation.
The first-time configuration typically includes:
- Accepting the End User License Agreement (EULA)
- Configuring network settings (NAT or routing mode)
- Setting default encryption parameters
- Defining DNS settings
- Creating initial user accounts
The web dashboard allows administrators to:
- Monitor connected users
- View session statistics
- Manage authentication methods
- Configure routing and access policies
One of the most important setup decisions is choosing between:
- NAT Mode – Easier setup, recommended for most environments
- Routing Mode – More advanced configuration for complex networks
NAT mode is generally preferred because it simplifies internal routing and minimizes configuration errors.
In diesem Stadium, enabling HTTPS certificates (either self-signed or trusted SSL certificates) is strongly recommended to secure the admin panel itself.
How to Configure Network Settings in OpenVPN Access Server
Network configuration determines how VPN clients access internal resources.
There are two main aspects to configure:
- VPN client subnet
- Access to internal private networks
You must define:
- The VPN subnet (e.g., 172.27.224.0/20)
- Whether clients can access the entire internal network
- Whether internet traffic should pass through the VPN (full tunnel)
- Or only internal traffic (split tunnel)
Full Tunnel vs Split Tunnel
- Full Tunnel: All client internet traffic goes through the VPN.
- Split Tunnel: Only traffic destined for internal resources uses the VPN.
Full tunnel improves security but increases bandwidth usage. Split tunnel improves performance but requires careful route configuration.
Administrators can also:
- Define static routes
- Assign access permissions per user
- Restrict specific subnets
- Apply firewall rules
Proper firewall configuration is critical. Ensure that required ports (UDP 1194 by default, TCP 443 if configured) are open and secured.
Misconfigured network rules can lead to:
- Inability to reach internal services
- DNS resolution issues
- Routing conflicts
Testing with a single user before company-wide rollout is strongly recommended.

Setting Up Admin Account and Secure Login Access
The admin account controls the entire OpenVPN Access Server environment, so securing it is crucial.
Best practices include:
- Changing the default password immediately
- Enabling strong password policies
- Activating two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Restricting admin panel access by IP (if possible)
- Using a trusted SSL certificate
In addition, consider:
- Disabling unused accounts
- Regularly reviewing active sessions
- Monitoring login attempts
- Enabling logging and audit trails
For larger environments, integration with LDAP or Active Directory allows centralized authentication management.
Security is layered. While VPN protects network access, other services such as email systems and application servers must also be hardened. If you are building a secure infrastructure on a VPS, you may also find our guide on Kali Linux VPS: Leistung, Privatsphäre, und Flexibilität Go insightful for advanced security testing and controlled environments
User Management and Authentication Methods in OpenVPN Access Server
Effective user management is one of the most critical components of deploying OpenVPN Access Server in a production environment. A VPN is only as secure as its authentication and access control mechanisms. Without proper user policies, even strong encryption cannot prevent unauthorized access caused by weak credentials or poor administrative oversight.
OpenVPN Access Server provides flexible user management options through its web-based Admin UI. Administrators can create individual users, assign passwords, define group memberships, and specify access permissions for particular subnets or services.
There are several authentication methods available:
- Local Authentication: Users are created directly within OpenVPN Access Server. Ideal for small teams or isolated environments.
- LDAP Integration: Allows integration with corporate directory services.
- Active Directory Authentication: Centralizes user credentials in Windows-based enterprise networks.
- RADIUS Authentication: Useful for organizations using external authentication servers.
- PAM Authentication: Leverages Linux system accounts.
smaller deployments
For smaller deployments, local authentication is simple and fast. Jedoch, enterprise environments benefit significantly from LDAP or Active Directory integration, which ensures that user lifecycle management (hire, role change, termination) remains centralized.
Administrators
Administrators can also assign users to groups. Group-based permissions allow consistent policy enforcement across departments. Zum Beispiel, developers may access staging servers, while finance staff can only access internal ERP systems.
Two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) should always be enabled whenever possible. By combining a password with a time-based one-time code (TOTP), you significantly reduce the risk of credential compromise.
Proper user management reduces the attack surface and ensures that VPN access remains controlled, überprüfbar, and aligned with organizational security policies.

Configuring VPN Client Profiles for Secure Connections
VPN client profiles define how end users connect to OpenVPN Access Server. These profiles contain configuration parameters such as server address, encryption settings, certificates, and routing instructions.
OpenVPN Access Server simplifies profile management through its Client Web UI. Users can log in and download pre-configured profiles tailored to their accounts. This eliminates manual configuration errors and ensures consistency.
Each client profile typically includes:
- Server hostname or IP address
- Port and protocol (UDP or TCP)
- Encryption parameters
- Certificate-based authentication (if enabled)
- Routing rules (split or full tunnel)
For enhanced security, administrators can enforce:
- Mandatory encryption standards
- TLS version requirements
- Certificate-based authentication
- Device-specific profile generation
Client profiles can be revoked instantly if a device is lost or compromised. This capability is crucial in modern remote work environments where employees may connect from multiple personal devices.
For organizations with strict compliance requirements, certificate-based authentication combined with 2FA offers strong identity assurance. Zusätzlich, limiting simultaneous logins per user reduces account sharing risks.
VPN client configuration is not just about connectivity—it is about ensuring encrypted, authenticated, and policy-compliant remote access.
Firewall and Port Configuration for OpenVPN Access Server
Proper firewall and port configuration is essential for a secure and stable OpenVPN Access Server deployment. Incorrect firewall rules are one of the most common causes of connectivity problems and security vulnerabilities.
By default, OpenVPN Access Server uses the following ports:
| Service | Default Port | Protokoll |
|---|---|---|
| VPN Tunnel (OpenVPN) | 1194 | UDP |
| HTTPS Admin & Client UI | 943 | TCP |
| HTTPS (Optional) | 443 | TCP |
You may customize these ports depending on your network security policies.
Key firewall best practices include:
- Allow inbound UDP 1194 (or your custom VPN port).
- Allow TCP 943 for Admin and Client UI access.
- Restrict Admin UI access to trusted IP ranges when possible.
- Block unnecessary inbound traffic.
- Enable outbound NAT if using NAT mode.
If deploying in cloud environments such as AWS, Azure, or other VPS providers, both the server firewall (iptables, firewalld, ufw) and cloud security group rules must be configured correctly.
It is also advisable to:
- Disable unused services.
- Use intrusion detection systems where applicable.
- Monitor firewall logs regularly.
Entsprechend Cloudflare:
A properly configured firewall is one of the most important layers in a defense-in-depth security strategy.
This highlights that VPN encryption alone is insufficient without strict perimeter controls.
When firewall rules are correctly configured, the VPN remains accessible while minimizing exposure to scanning, brute-force attempts, and network probing.
How to Connect Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS Clients
OpenVPN Access Server supports a wide range of operating systems, making it suitable for heterogeneous environments.
Windows
Users can download the OpenVPN Connect client directly from the Client Web UI. Nach der Installation:
- Import the user profile file.
- Enter credentials.
- Connect securely.
Windows users benefit from automatic route injection and DNS configuration.
macOS
macOS clients follow a similar process using OpenVPN Connect. The configuration file ensures seamless integration with macOS networking settings.
Android
Android users install OpenVPN Connect from Google Play. After importing the profile:
- Enter username and password.
- Approve connection permissions.
- Establish secure tunnel.
Mobile VPN connections are especially important when users access resources over public Wi-Fi networks.
iOS
iOS users install the OpenVPN Connect app from the App Store. Profiles can be downloaded directly from the Client UI or imported manually.
For all platforms, administrators should:
- Enforce strong passwords.
- Enable 2FA.
- Restrict simultaneous sessions.
- Encourage users to disconnect when not in use.
Cross-platform support ensures consistent security policies across desktops, laptops, and mobile devices.
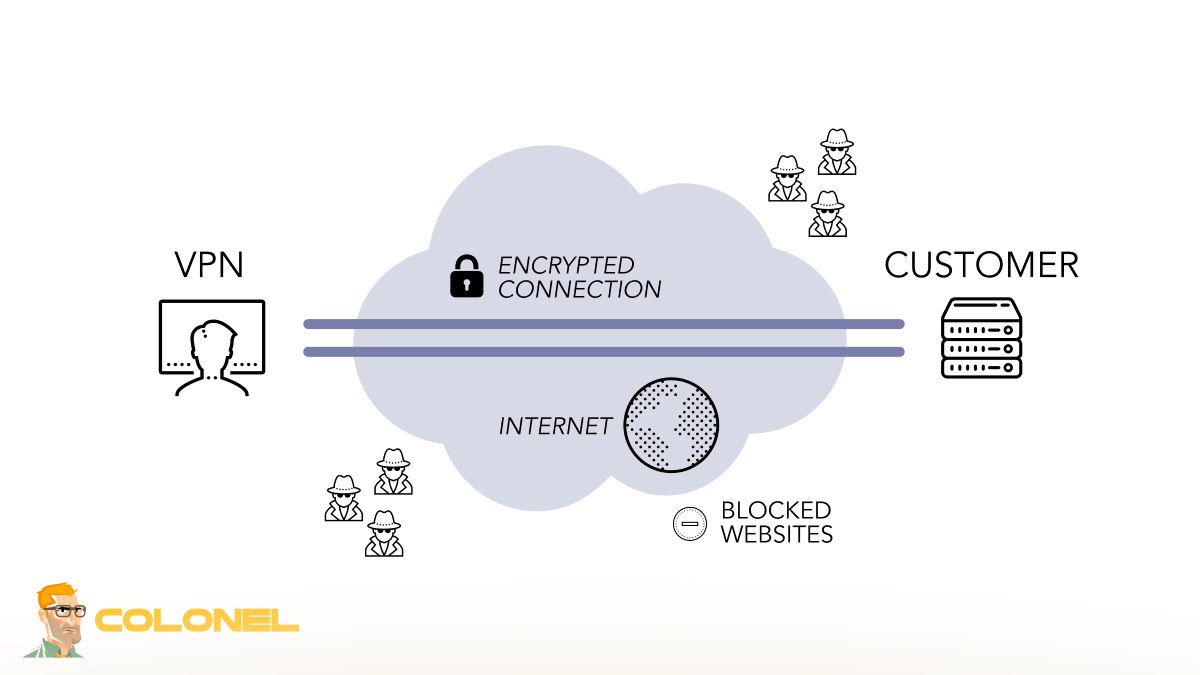
Testing and Verifying Your OpenVPN VPN Connection
After deployment, thorough testing ensures your VPN operates securely and efficiently.
Testing should include:
- Verifying successful client authentication
- Checking internal resource access
- Confirming DNS resolution
- Ensuring encryption is active
- Testing split vs full tunnel behavior
You can validate encryption by checking the client logs or verifying your public IP address while connected.
Additional tests include:
- Attempting unauthorized login attempts
- Testing firewall restrictions
- Verifying subnet accessibility
- Monitoring session logs
Administrators should also simulate real-world scenarios such as connecting from different ISPs or mobile networks.
Regular verification ensures that configuration changes, Aktualisierungen, or firewall adjustments have not disrupted connectivity or weakened security.
OpenVPN Access Server Security Best Practices
Deploying OpenVPN Access Server securely requires more than installation. Ongoing hardening is essential.
Security best practices include:
- Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Using strong encryption standards
- Updating regularly
- Restricting Admin UI access
- Monitoring logs and connection history
- Limiting user permissions
- Revoking unused accounts immediately
- Using trusted SSL certificates
Administrators should adopt a principle of least privilege—users should only access resources necessary for their roles.
Zusätzlich, consider:
- Enabling brute-force protection
- Using fail2ban (if applicable)
- Implementing IP whitelisting for admin access
Security is not a one-time setup; it is an ongoing process that requires monitoring, Aktualisierungen, and policy enforcement.
Troubleshooting Common OpenVPN Access Server Issues
Even well-configured deployments may encounter issues. Understanding common problems accelerates resolution.
Common issues include:
- Connection timeout errors
- Incorrect credentials
- Firewall blocking UDP traffic
- DNS resolution failures
- Routing conflicts
- TLS handshake errors
Troubleshooting steps:
Check server service status.
- Review server logs.
- Confirm firewall rules.
- Validate client profile settings.
- Ensure correct system time (important for TLS).
Log files are the primary diagnostic tool. Most connection failures stem from firewall misconfiguration or incorrect routing settings. Testing connectivity step-by-step—from network reachability to authentication—helps isolate the issue quickly.
How to Update and Maintain OpenVPN Access Server
Regular updates are critical to maintain security and performance. OpenVPN periodically releases patches for security vulnerabilities, performance improvements, and feature enhancements.
Maintenance tasks include:
Updating the Access Server package
- Applying OS security patches
- Reviewing user accounts
- Checking certificate validity
- Backing up configuration settings
- Monitoring system resources
Before updating in production:
Create backups.
- Test in staging environment if possible.
- Schedule maintenance windows.
- Routine maintenance prevents unexpected downtime and ensures compliance with security best practices.
Abschluss
OpenVPN Access Server provides a comprehensive and secure framework for remote access management. From advanced user authentication and client profile configuration to firewall integration and cross-platform compatibility, it offers organizations a scalable solution for encrypted connectivity.
By implementing strong authentication methods, carefully configuring firewall rules, enabling 2FA, and maintaining regular updates, businesses can build a secure remote access infrastructure that protects sensitive data while enabling flexible work environments.
Ongoing monitoring, testing, and policy enforcement ensure that OpenVPN Access Server remains not just operational—but resilient against modern cybersecurity threats.
