
Reducing Time to First Byte on VPS hosting means minimizing the delay between a user request and the moment your server sends its first byte of data. This metric directly reflects server responsiveness and backend efficiency, making it one of the most important indicators of real-world website performance.
On hosting environments like Duitsland VPS, TTFB becomes even more critical because server resources, configuration quality, and geographic placement play a direct role in response time. Unlike shared hosting, VPS environments give you control over CPU, geheugen, en softwarestack, which also means responsibility for optimization. If your goal is to reduce TTFB server response times consistently, you must focus on infrastructure-level improvements rather than surface-level frontend tweaks.
Understanding Time to First Byte (TTFB)
Time to First Byte refers to the time elapsed between a client sending an HTTP request and receiving the first byte of data from the server. It does not measure full page load time; instead, it isolates server responsiveness and network efficiency before rendering begins. TTFB consists of three sequential phases:
- request transmission
- server processing
- initial response delivery
Each phase introduces potential delays, especially on VPS environments where server configuration, backend logic, and geographic location are under direct control of the site owner. When the goal is to reduce TTFB server latency, optimizing these upstream phases becomes more impactful than frontend performance tuning.
Why TTFB Is a Critical Metric for VPS Performance?
TTFB directly determines how fast users perceive your website to be because it governs the moment when the browser receives its first response. Even a delay of a few hundred milliseconds at this stage can significantly increase bounce rates, especially for mobile and international visitors.
From an SEO perspective, Google treats server responsiveness as a quality signal. High TTFB can negatively affect Core Web Vitals by delaying:

WordPress-webhosting
Vanaf $ 3,99/maandelijks
- First Contentful Paint (FCP)
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
On VPS hosting, where performance responsibility lies primarily with the site owner, failing to reduce TTFB server delays can undermine otherwise well-optimized content and technical SEO efforts.
Beyond rankings, TTFB also functions as a scalability indicator. A rising TTFB under moderate traffic often signals resource contention, inefficient backend execution, or insufficient VPS capacity. Addressing TTFB early prevents performance degradation as traffic grows.

What Is Considered a Good TTFB on VPS Hosting?
A good TTFB on VPS hosting depends on application type, geographic distribution, and workload complexity, but there are widely accepted benchmarks that define healthy performance.
- For most VPS-hosted websites, a TTFB below 200 milliseconds indicates excellent server responsiveness and efficient request handling.
- Values between 200 and 500 milliseconds are generally acceptable, especially for dynamic applications.
- When TTFB exceeds 800 milliseconds consistently, it suggests systemic inefficiencies that require architectural or infrastructure-level changes to reduce TTFB server latency.
Static websites often achieve lower TTFB because they avoid backend processing overhead, while dynamic platforms such as CMS-driven sites typically stabilize between 200 and 300 milliseconds even after optimization. These benchmarks provide a practical baseline for evaluating whether a VPS environment is performing competitively.
Factors Affecting Time to First Byte on VPS Servers
Several interdependent factors influence TTFB on VPS hosting, and improving server responsiveness requires understanding how each component contributes to the delay. These factors are not interchangeable; each one affects a different stage of the request lifecycle.

Goedkope VPS-server
Vanaf $ 2,99/maandelijks
Server Processing Efficiency
Server processing time is one of the most dominant contributors to high TTFB. When a request reaches the VPS, the server must execute application logic, interact with databases, and generate a response. Inefficient code paths, excessive middleware layers, or poorly optimized backend frameworks significantly slow this process.
In VPS environments, insufficient CPU allocation or memory pressure can amplify these delays. If the server struggles to process concurrent requests, TTFB increases even before network latency becomes relevant. Reducing TTFB server overhead, therefore, requires careful attention to backend execution efficiency.

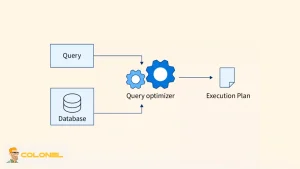
Database Performance and Query Design
Database operations frequently dominate backend processing time, especially for dynamic websites. Unindexed queries, complex joins, and redundant data access patterns force the server to wait before it can begin sending a response.
Even powerful VPS configurations suffer from high TTFB if database queries are poorly designed. Query optimization, indexing strategies, and caching mechanisms directly reduce backend wait time, enabling the server to respond faster. In many real-world cases, improving database performance yields the most immediate reduction in TTFB server metrics.
Network Latency and Physical Distance
The physical distance between the VPS data center and the end user introduces unavoidable latency. Each request must travel across multiple network hops before reaching the server, and the response must return the same way.

Windows VPS-hosting
Remote Access & Full Admin
On VPS hosting, selecting an appropriate data center location is a foundational decision. Even a perfectly optimized server cannot deliver low TTFB to distant users without addressing network latency. This is why global traffic patterns play a central role when attempting to reduce TTFB server response times consistently.
DNS Resolution Time
Before a request reaches the VPS, the browser must resolve the domain name into an IP address. Slow DNS providers or misconfigured DNS settings introduce a delay before server processing even begins.
Although DNS resolution represents a smaller portion of TTFB compared to backend execution, it becomes significant for first-time visitors and uncached requests. Reliable DNS infrastructure supports faster request initiation and contributes to lowering overall TTFB server measurements.
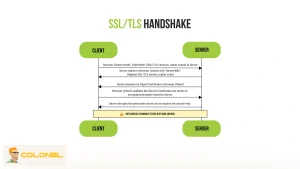
TLS Handshake and Secure Connections
Secure HTTPS connections require additional negotiation steps before data transfer begins. Each TLS handshake adds round-trip time that increases initial response time, particularly on older protocol versions or misconfigured servers.
On VPS hosting, inefficient TLS settings or a lack of session reuse can inflate TTFB unnecessarily. While security cannot be compromised, optimizing encryption configuration helps reduce TTFB server overhead without weakening protection.
Traffic Load and Resource Contention
As traffic increases, VPS resources are shared among more concurrent processes. When CPU, geheugen, or disk I/O limits are reached, requests queue instead of being processed immediately, raising TTFB.
This effect is especially pronounced on under-provisioned VPS plans. Monitoring TTFB under load provides early warning signs of scalability limits and helps administrators determine when to optimize or upgrade infrastructure to maintain consistent responsiveness.
How TTFB Relates to Other Performance Metrics
TTFB acts as an upstream dependency for nearly all browser-level performance indicators. Metrics such as First Contentful Paint and Largest Contentful Paint cannot improve if the server fails to respond promptly.
Faster initial responses allow browsers to start rendering sooner, improving user perception even if total load time remains unchanged. This is why TTFB optimization often produces disproportionate gains in perceived speed compared to frontend adjustments.
According to Google’s web performance documentation, “Server response time directly impacts how quickly a page can start rendering, affecting both user experience and Core Web Vitals performance.”
Strategic Approach to Reducing TTFB on VPS Hosting
Reducing TTFB on a server requires a backend-first mindset because Time to First Byte is determined before frontend assets even begin loading. Unlike general speed optimization, TTFB improvement focuses on how fast the VPS accepts, processes, and responds to requests under real conditions.
The following strategies address the most impactful layers involved in reducing TTFB server latency.
Optimize VPS Server Configuration for Faster Initial Responses
Server configuration is the foundation of TTFB performance because every request must pass through the operating system, web server, and runtime environment before processing begins. Poor defaults or bloated configurations introduce latency even on powerful hardware.
A VPS optimized for low TTFB uses lightweight web servers, tuned worker processes, and efficient connection handling. Removing unused modules, adjusting keep-alive settings, and aligning server resources with traffic patterns significantly reduces request queuing. When administrators aim to reduce TTFB server delays, configuration optimization consistently delivers immediate gains without code changes.

Use Multi-Layer Caching to Eliminate Backend Processing Delays
Caching reduces TTFB by preventing the VPS from executing full backend logic for every request. Instead of generating responses dynamically, cached content is served immediately, allowing the first byte to reach the client faster.
Caching strategies vary depending on application complexity. Page caching serves complete HTML responses, object caching accelerates database queries, and opcode caching speeds up script execution. On VPS hosting, combining these layers avoids reliance on a single cache mechanism and ensures consistent performance under load. Effective caching directly reduces TTFB server response time by minimizing server-side computation.
Leverage CDN Integration to Reduce Geographic Latency
Geographic distance is a structural contributor to high TTFB, especially for global audiences. A Content Delivery Network reduces this latency by serving cached content from edge locations closer to users.
While dynamic requests may still reach the VPS origin, CDNs significantly reduce TTFB for cacheable responses and static elements. Additionally, offloading traffic to the edge decreases origin server load, indirectly improving TTFB for uncached requests. For VPS-hosted websites targeting international users, CDN integration is one of the most reliable ways to reduce TTFB server variability across regions.
Optimize Database Execution Paths for Faster Backend Responses
Database latency often dominates backend processing time, making it a critical factor when reducing TTFB on VPS environments. Slow queries delay response generation even when server resources are sufficient.
Improving database performance involves indexing frequently accessed fields, reducing complex joins, and caching query results where appropriate. Query profiling helps identify execution bottlenecks that inflate TTFB. When database operations are optimized, the VPS can generate responses faster, directly lowering TTFB server metrics across dynamic pages.
Reduce Application-Level Processing Overhead
Backend application logic determines how much work the server performs before responding. Excessive middleware layers, synchronous external API calls, and heavy data transformations increase TTFB unnecessarily.
Reducing processing overhead requires auditing request lifecycles and eliminating non-critical operations from the critical path. Asynchronous processing and deferred tasks allow the server to respond sooner while completing additional work in the background. For VPS-hosted applications, simplifying backend execution is one of the most effective ways to reduce TTFB server delays without upgrading infrastructure.
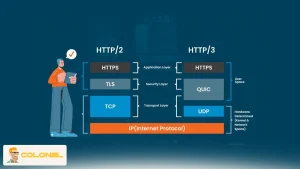
Enable Modern Protocols to Improve Connection Efficiency
Transport protocols influence how quickly requests are established and responses begin. Legacy protocols like HTTP/1.1 introduce head-of-line blocking that delays initial responses.
Enabling HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 allows multiplexing, connection reuse, and faster negotiation, which improves TTFB at the transport layer. On VPS hosting, protocol upgrades are low-effort changes that deliver measurable improvements in server responsiveness. These protocols reduce connection overhead and help reduce TTFB server latency even before application processing begins.
Minimize Redirect Chains and Request Hops
Redirects delay the delivery of the first byte by forcing additional request-response cycles before reaching the final resource. Each redirect adds latency, particularly noticeable on mobile networks.
Reducing unnecessary redirects improves TTFB by allowing the browser to reach the VPS origin directly. Ensuring canonical URLs, consolidating redirect rules, and avoiding protocol-based redirect chains removes avoidable delays. This optimization is simple yet highly effective when the goal is to reduce TTFB server response times.
Monitor TTFB Continuously in Real-World Conditions
TTFB optimization is not a one-time task because server performance changes with traffic patterns, deployments, and infrastructure updates. Continuous monitoring ensures improvements persist over time.
Using synthetic monitoring and real user monitoring (RUM) allows administrators to track TTFB across locations and devices. Alerts for sudden TTFB spikes help identify backend regressions early. For VPS environments, ongoing visibility into TTFB ensures that server responsiveness remains stable as workloads evolve.
Final Perspective on Optimizing TTFB
Time to First Byte is not an isolated performance metric but a direct reflection of how efficiently the entire request–response chain operates. From DNS resolution and server processing to backend logic and database performance, every architectural decision influences how quickly the first byte reaches the user. Poor TTFB often signals deeper infrastructural or configuration weaknesses rather than a superficial speed issue.
Long-term TTFB optimization requires a balanced approach that combines server-level tuning, intelligent caching strategies, efficient application logic, and geographically aware delivery mechanisms. Improvements become sustainable only when monitoring, testing, and performance validation are treated as ongoing processes rather than one-time optimizations. When addressed holistically, TTFB improvements translate into faster perceived load times, stronger SEO signals, and a noticeably better user experience across both desktop and mobile environments.
TTFB Optimization Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the fastest way to reduce TTFB on a VPS?
The fastest way to reduce TTFB server delays is to implement server-side caching and optimize backend processing. These changes eliminate unnecessary computation before the first byte is sent.
Does upgrading VPS resources always improve TTFB?
Upgrading resources can help, but it does not guarantee lower TTFB if server configuration, database performance, or application logic remain inefficient.
Can a CDN fully eliminate high TTFB?
A CDN significantly reduces TTFB for cached and static content, but dynamic requests still depend on VPS backend performance and configuration.
Is TTFB more important than full page load time?
TTFB sets the baseline for all other performance metrics. A slow TTFB delays rendering regardless of frontend optimization, making it a foundational metric.
